Notes from Demos for Haptic Symposium Visitors
Posted: March 11, 2012 Filed under: Uncategorized Comments Off on Notes from Demos for Haptic Symposium Visitors“All make [the phone] seem alive”
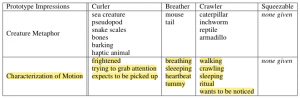
Vibrate/waddle: snoring, purring, more whimsical ring, pleasant
Vibrate: buzzing, ramps up/down more smoothly than a regular phone, shivering/cold
Waddle: cat-like when it does it by itself
Breathing: nervous, beating, creature inside, something beating, organic, artificial heart, heart beat, nervous, breathing, creature trying to get out, tapping/poking, know it’s a servo …feels uneven (to be breathing it needs to be more smooth), the click when it goes down make makes it feel artificial
Ears wiggle: pay attention to me, happy, it’s wiggling its ears, wagging its tail, sounds angry
…when they hold it at the ears end, the other end moves
Ears that move once: pay attention to me when you have time, don’t touch me here, reptilian, muscle tension, curling up
Hot/cold: cell phones already get hot – normal plugged in electronic
Foam: Very pleasant to touch. Could communicate differently than if they were made of plastic
Random Notes/Suggestions:
Almost everyone pushed down hard on the prototype
Add a string gauge…. measures the deformation of a device
Possible reference: Matthew Bowman, Tom Hazelton …emulating attention getting …would be a good reference (emotion expression stuff)
In the area of Organic Haptics
One ‘mode’/area’ we are exploring is Shape changing.
Prof. Hiroshi Ishiguro …doing similar research
Meeting Notes – March 1, 2012
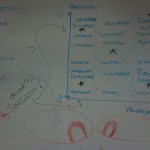
Posted: March 2, 2012 Filed under: Uncategorized Comments Off on Meeting Notes – March 1, 2012ANGRY / DISTRESSED (NEGATIVE VALENCE, HIGH AROUSAL)
- fast/strong vibrate or breathing, and heat
- red
- red and fast vibrate/breathing
- ears/body shape and breathing/vibrate
- tense and breathing/vibrate and red
- texture??
- puffed up
EXCITED (POSITIVE VALENCE, HIGH AROUSAL)
- perked ears and breathing/vibrate
- large/slow vibration (waddle/rock)
- color/rainbow (fast color change) and vibrate/breathing
NEUTRAL/AWARE
If the phone is always moving (during neutral), are people more likely to interpret this as the phone’s emotions vs other people emotions?
– living neutral vs phone neutral/phone off
How to then convey neutral text messages?
Can we separate neutral and relaxed?
- even breathing
- twitch ears slowly
- shrugging (corners go up or come together)
- slightly cool?
RELAXED (POSITIVE VALENCE, LOW AROUSAL)
- untensed/expanded
- slow breathing
- warm
DEPRESSED / COLD/ICY
- cold
OUR BIG FOUR
Vibrate (small and large)
Temperature
Breathing
Ears
Maybe add color and noise later… as a way of helping it along, help people tell them apart …can be a kind of visual illusion
PROTOTYPES
Ears (mechanized or puppet)
Breathing (mechanized)
Vibrate and temperature (mechanized)
DIMENSIONS
For now, aim for one inch wider and one inch longer than iPhone dimensions
All the prototypes are currently 13cm x 7cm
SHOPPING LIST
- peltier plate or two
- heat sink
- small buzzers
- smaller servos
- small unenclosed vibrator
Meeting Notes – February 27, 2012
Posted: March 2, 2012 Filed under: Uncategorized Comments Off on Meeting Notes – February 27, 2012
Discussion with Oliver (Jessica)
– Oliver looked at the phone expressing the phone’s emotion. Found that people can interpret phone’s emotion. Makes sense to look at how we can get people to interpret the emotions as someone else’s emotions (via the phone)… could just be a context thing, like making the phone ring.
– Were able to get some negative emotions (scared, creepy, etc)
– positive valence and high arousal would probably be easier to communicate (people like to interpret things as happy… Jessica and Oliver’s opinion) …Oliver found that the really animated one were negative
Heikkinen 2009
– if people receive a emotional message they want to be able to reciprocate
– section 4.2.2 is most important/relevant
– communicating emotion just using touch
– concerned about privacy …we may still be concerned with privacy (but maybe for different reasons)
Other paper Jessica read
– emotional expressivity
– interpreting people’s body movements as a way to express emotion
– talk about how to characterize things
– sent crazy color pictures to people
Ways to pick emotions
– pick emotions that give us good coverage of the chart
– pick emotions commonly expressed in emails/texts
– pick emotions that would be easiest to express with a phone
– Looking at the four corners of the emotion quadrant for now… keep things really far apart for now… see where there might be blending, or where differentiation is needed, then adjust what emotions we’re focusing on.
– intimate messages (love, etc) might be important to explore… fall under ‘pleased’
Literature Review
Posted: February 27, 2012 Filed under: Uncategorized 2 Comments »To keep track of what each of us has read for our lit review…
Juliette:
Introducing the HiPhone (Oliver Schneider et al.) Oliver looked at “emotion” in terms of…
Take me by the hand: haptic compasses in mobile devices through shape change and weight shift (Fabian Hemmert et al.) Looks at shape change and weight shift for navigational purposes.
Shape-changing mobiles: Tapering in one-dimensional deformation displays in mobile phones (Fabian Hemmert et al.) This is the paper where they change the tapering of the back panel of the phone. Applications: interactive feedback (e.g. scrolling), user notification (e.g. file download status), ambient display (e.g. battery status). Visual and blind user study, looking at accuracy of determining panel angle.
Ambient life: Calm and excited pulsation as a means of life-like permanent tactile status display in mobile phones (Fabian Hemmert and Gesche Joost) In this paper we present Ambient Life, a novel notification system for mobile phones (focuses on ambient display). It is based on a cognitive mechanism that humans are inherently good at: the perception of life. The proposed system employs basic life-like movements, like breath and pulse, to display the state of a mobile phone. The phone can either be “calm” (representing no missed calls, SMS or similar) or “excited” (representing missed events, requiring attention). Two prototypes and a user study are presented. The outcomes of the study are mixed; while most users generally liked the idea of a living phone and were able to determine changes in the pulse frequency almost instantly, the acceptance of the new functionality depended strongly on the situation the phone was used in.
- The system simulates excitement (high pulse, as for a missed call/sms/appointment) and, more importantly, calmness (normal pulse, i.e. as for sufficient battery, good network reception, and no missed events). Opposed to all other mobile phones, it actively communicates that everything is fine, and that there is no need to check it.
- Interesting idea of using a mobile shaped shell.
- Interpretation varied across situations (in hand vs afar vs in pocket), people founds pulsing annoying.
Physical embodiments for mobile communication agents. (Stefan Marti and Chris Schmandt) This is the paper where they made a furry squirrel into a phone.
Designing cally,: a cell-phone robot. (Ji-Dong Yim and Christopher D. Shaw) This is the paper where they stuck a phone on a robot body. They had an interesting pilot project where they had people dress up like phones.
Thanks Tail video – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=47CX3hjpjRk
Shathel:
Evaluation of Unsupervised Emotion Models to Textual Affect Recognition: provides techniques for detecting emotions in text
Expectations for User Experience in Haptic Communication with Mobile Devices: adminstered focus groups to study user expectations of haptic interaction on mobile devices.
Expressing Emotion in Text-based Communication: how users differentiate between negative and positive affect in text-based content


Recent Comments